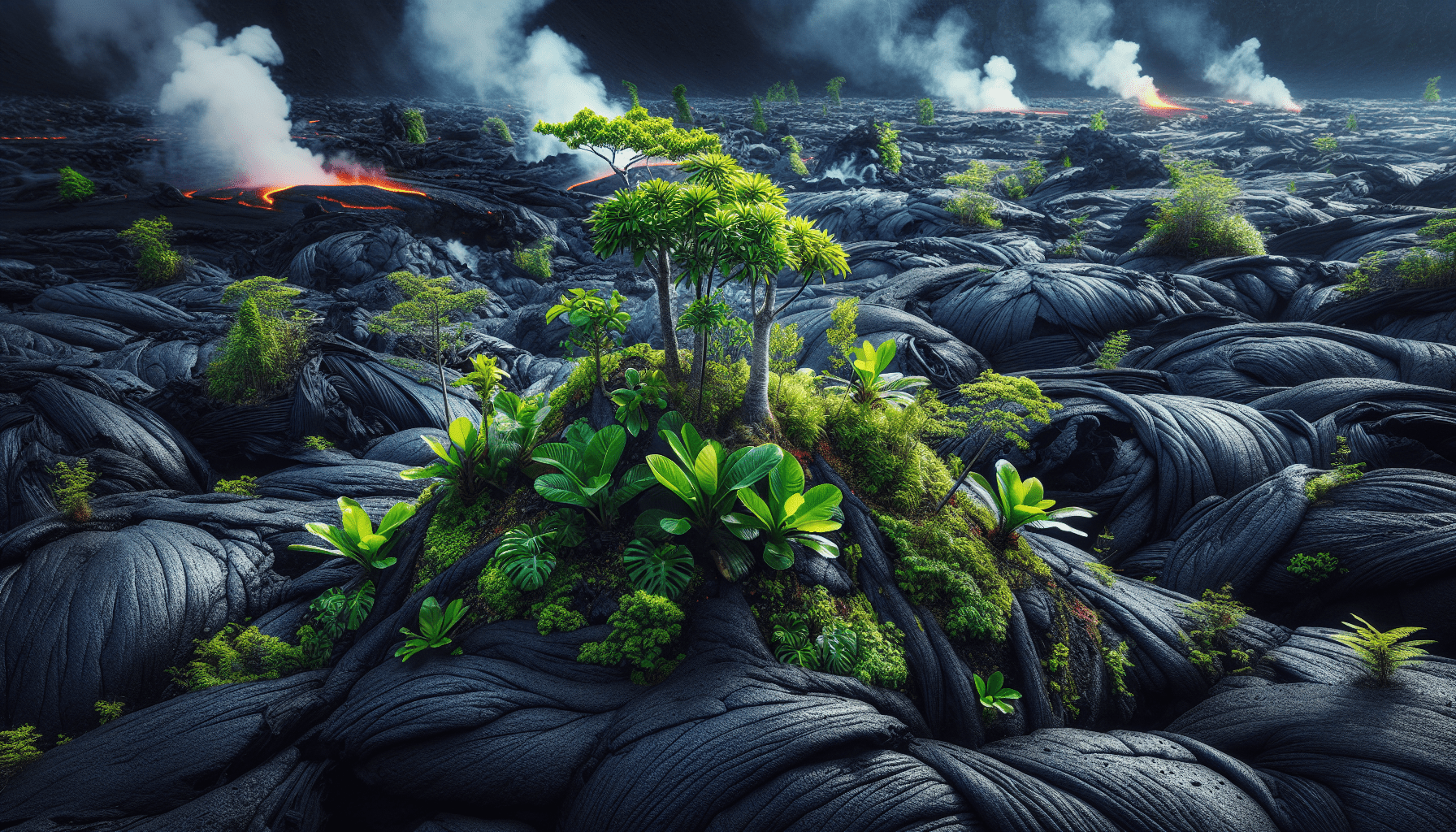
Have you ever wondered what role volcanic activity plays in shaping and supporting life on Earth? This question might not cross your mind often. Still, it’s fascinating to consider how something as destructive as a volcano could contribute positively to the rich tapestry of life we see around us. Volcanos are not just fiery mountains that spew ash and lava across landscapes. They are dynamic forces that have shaped and fueled biodiversity in ways you might not have considered.
Understanding Volcanic Activity
Volcanic activity is a natural phenomenon that occurs when there is an eruption of lava, ash, and gases from a volcano. This activity is driven by the intense heat and pressure found beneath Earth’s surface. It’s amazing to think about how these fiery events, starting from deep within our planet, can influence everything above ground—even life itself.
The Mechanics of a Volcano
At the heart of volcanic activity lies the movement of Earth’s tectonic plates. Picture these plates as enormous slabs that float atop the molten rock in our planet’s mantle. When these plates shift, they can create spaces for magma to push through, resulting in an explosion we witness as a volcanic eruption. Intricate, isn’t it? The magma, once it breaks through, becomes known as lava, and it sprawls across the land, creating new geological formations.
Types of Volcanoes and Eruptions
Different types of volcanoes and eruptions have distinct effects on the environment. You have your shield volcanoes, which ooze lava slowly across vast distances, and composite volcanoes, which are far more explosive, sending clouds of ash high into the atmosphere. Each eruption type influences the environment in unique ways, altering ecosystems and, ultimately, biodiversity.
Volcanic Activity’s Initial Impact on Life
At first glance, you might think that volcanic eruptions only bring destruction. Indeed, the immediate aftermath of an eruption is usually devastating to local ecosystems. Lava flows incinerate everything in their path, and ash clouds can cover entire landscapes. Yet, beneath the surface of this destruction lies an unexpected potential for life.
The Aftermath: Destruction Leads to Creation
Once the dust—or ash—settles, the barren land left behind offers a blank canvas for life to reclaim. The first organisms to colonize these areas are often hardy pioneer species, like certain types of bacteria and plants, that can withstand poor soil and harsh conditions. These pioneers start the process of ecological succession, gradually transforming the volcanic landscape into thriving ecosystems over time.
Contribution to Soil Fertility
Interestingly, volcanic ash plays a crucial role in rejuvenating soil. It is rich in minerals that are slowly broken down by weathering processes, providing essential nutrients that plants need to thrive. Over decades and centuries, these nutrients enrich the soil, allowing more complex plant life to take root. It’s a slow, steady process that underscores nature’s remarkable resilience.
Volcanic Ecosystems
The ecosystems that develop around volcanoes are often unique, inhabited by species adapted to specific conditions of these environments. These ecosystems are like hidden gems of biodiversity, showcasing the adaptability and resourcefulness of life.
Flora and Fauna of Volcanic Landscapes
Once the soil is enriched with nutrients, a cascade of life follows. Ferns, lichens, and shrubs begin to appear, creating a habitat for various animal species. Over time, these areas can support entire forests home to diverse wildlife. In some places, volcanic islands form crucial sanctuaries for endangered species, providing isolated environments where they can thrive without invasive predators.
Adaptations to Volcanic Environments
Species living in volcanic regions often develop unique adaptations. For instance, certain plants may evolve to be more tolerant of sulfuric soils, while animals might adapt behaviors to deal with frequent ashfall. These unique traits enrich Earth’s biodiversity and highlight the ingenious ways life can evolve in challenging conditions.
Volcanic Activity Through Geological Time
Taking a step back in time offers a broader perspective on how volcanic activity has shaped biodiversity throughout Earth’s history. Ancient volcanic events have left long-lasting impacts, contributing significantly to the planet’s biological richness.
Historical Significance
Some of the most massive eruptions in Earth’s history have caused global climate shifts, playing a role in the evolution and diversification of life. For example, the eruption of the Deccan Traps in what is now India around 66 million years ago coincided with the mass extinction event that led to the demise of the dinosaurs. This paved the way for mammals to rise and diversify.
Islands Born of Fire
Volcanic activity has given birth to islands, which serve as incubators of unique biodiversity. The Galápagos Islands, for instance, are a result of volcanic activity and are home to species found nowhere else on Earth. These islands provide critical insights into evolution and have inspired pivotal scientific studies, such as Charles Darwin’s theory of natural selection.
| Volcanic Contributions to Biodiversity | Examples of Impact |
|---|---|
| Fertile Soil Formation | Nutrient-rich soils support diverse plant life, fueling entire ecosystems. |
| Island Formation | Creation of isolated habitats, leading to species diversity and evolution. |
| Habitat Creation | New ecosystems in barren volcanic landscapes support unique flora and fauna. |
Human Impact and Volcanic Ecosystems
Humans are not merely passive observers of volcanic activity. Our species has learned to live alongside volcanoes, even utilizing them to our benefit. Yet, we also pose threats to these delicate environments.
Reaping the Benefits
People have inhabited volcanic regions for centuries, drawn by the fertile soils. Farming communities thrive in these areas, producing abundant crops thanks to the rich volcanic earth. Additionally, geothermal energy from volcanic areas has become an important renewable resource, showcasing how we can harness natural forces sustainably.
Conservation Challenges
Volcanic regions pose unique conservation challenges. The delicate balance of these ecosystems can be upset by human activities such as tourism, mining, and deforestation. Careful management is crucial to ensure that these biodiverse areas remain preserved for future generations while allowing human communities to benefit sustainably.
Volcanic Activity and Climate
While volcanic eruptions are primarily a geological event, they significantly influence the Earth’s climate system, which in turn affects biodiversity. Understanding these interactions helps illuminate the complex web of forces that govern life on our planet.
Short-term Climate Effects
Volcanic eruptions can inject massive amounts of ash and gases like sulfur dioxide into the atmosphere, leading to temporary climate cooling. This occurs because these particles block sunlight, reducing global temperatures. Ironically, the cooling effect can sometimes be beneficial for some species, providing temporary reprieve during periods of global warming.
Long-term Climate and Biodiversity
Over geological timescales, volcanic activity contributes to carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere, influencing global climate trends. This has a downstream effect on biodiversity, as climate shifts necessitate adaptation, migration, or extinction of species. These periods of climate upheaval have historically resulted in significant biological turnover and the emergence of new species.
The Future of Volcanic Activity and Biodiversity
As we look towards the future, it becomes crucial to consider how ongoing volcanic activity will continue to shape Earth’s biodiversity in the context of human-induced climate change and environmental challenges.
Understanding Risks and Opportunities
Volcanic eruptions will undoubtedly continue to occur, providing both risks and opportunities for biodiversity. Scientists are focusing on improving eruption forecasting to mitigate risks to human and ecological communities. Concurrently, understanding the role of volcanoes in carbon capture and sequestration could offer pathways to mitigate climate change impacts.
Conservation and Research Priorities
Preserving the unique ecosystems nurtured by volcanic activity should be a priority. Mindful conservation efforts can help protect these landscapes from degradation while allowing for scientific research to continue unraveling the mysteries of biodiversity and evolution. Such efforts will ensure that volcanoes remain a vital part of Earth’s ecological tapestry.
A Catalyst for Life
Reflecting on the complex interplay between volcanic activity and biodiversity, it becomes clear that volcanoes are far more than sources of destruction. They are catalysts for life, shaping our world in ways both subtle and profound. Their eruptions, while devastating in the short term, offer new opportunities for ecosystems to emerge and diversify.
Whether it’s the formation of fertile soils, the creation of new islands, or the intricate adaptations seen in volcanic ecosystems, these fiery giants hold a timeless role in the saga of life on Earth. Understanding this connection not only deepens our appreciation for the natural world but also enhances our ability to live harmoniously with these powerful natural phenomena.
So, next time you hear about a volcanic eruption, think beyond the ash clouds and lava flows. Consider its lasting contribution to the intricate web of life that defines our planet. In the fiery breath of a volcano, you might just glimpse the resilience and creativity of nature itself.